What is a Laparoscopic Oophorectomy?

A laparoscopic oophorectomy (pronounced “oh-uff-uh-RECK-tomy”) is the removal of one or both ovaries via a minimally invasive surgical technique using a few small incisions.
Your ovaries are a pair of walnut-sized organs that lie at the end of your Fallopian tubes on either side of your uterus.
Ovaries not only contain your eggs but also produce estrogen and progesterone: two hormones essential for menstruation and pregnancy.
Why are Oophorectomies done?
Oophorectomies are necessary when your ovaries (and frequently, nearby organs and surrounding tissues) become diseased. One or both ovaries might need to be removed, although it is not uncommon for women to undergo additional procedures at the same time as the removal of the ovary, such as a hysterectomy (uterus removal) or salpingectomy (fallopian tube removal).
There are several gynecologic conditions that might warrant an oophorectomy, including:
- Ovarian cancer
- Non-cancerous ovarian tumors
- Ovarian cysts
- Ovarian torsion (when an ovary twists on its stalk)
- Tubo-ovarian abscesses (when pus pockets form on the ovaries and fallopian tubes)
Watch Dr. Aliabadi remove an 8-pound fibroid tumor laparoscopically on The Doctors TV Show.
How does an Oophorectomy affect fertility?
If you have a unilateral oophorectomy, where only one ovary is removed, you could continue to menstruate after surgery and conceive naturally.
If you undergo bilateral oophorectomy, in which both of your ovaries are removed, you will no longer produce estrogen and your periods will stop, putting you into early, or premature, menopause.
Premature menopause can result in the following symptoms and complications:
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Vaginal dryness and pain with intercourse
- Decreased libido
- Memory problems
- Depression and/or anxiety
- A decline in bone density
Luckily, these symptoms may be treated. You can discuss your concerns with us and we will, of course, review post-op treatment options with you.
Having a bilateral oophorectomy means that you will no longer be able to get pregnant naturally, although you still may be able to carry a child using assisted reproductive techniques, such as in-vitro fertilization or egg donation. If you would still like to have children after a bilateral oophorectomy, we can refer you to a fertility specialist.
Preparing for a Laparoscopic Oophorectomy
The decision to remove your ovaries is not one that is taken lightly. We recommend the removal of an ovary only after diagnostic testing has confirmed that the ovary is diseased and must be removed for the sake of your health.
We may use one or more of the following tests in order to diagnose your condition:
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound is a painless non-invasive test that involves passing a wand over your abdomen which has been coated with a gel to facilitate gliding. By tracking sound waves, we can determine the shape, size, and composition of your ovaries and surrounding organs, such as your uterus and fallopian tubes.
- MRI/CT Scan: Both of these imaging studies provide us with a more detailed view of your pelvic cavity using either magnetic fields or radiation.
- Blood Tests: We may order a number of blood tests to help guide our diagnosis and surgical decisions. These can include a pregnancy test (if there’s any possibility that you might be pregnant), check your hormone levels (as that may play a role in tumor growth), and measure your CA-125 protein levels (which can be high in the presence of ovarian cancer).
What happens during a Laparoscopic Oophorectomy?
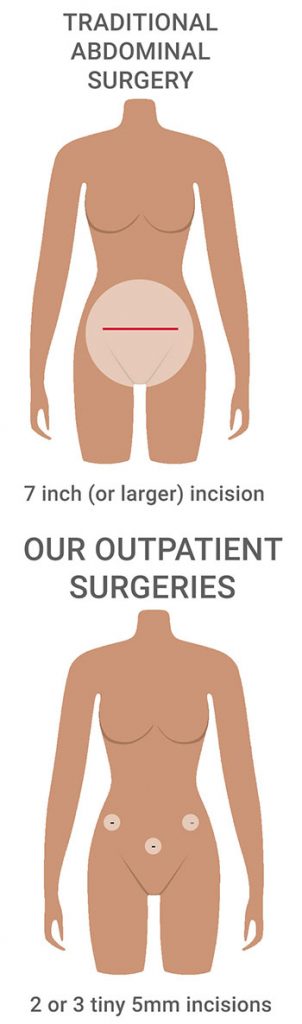
A laparoscopic oophorectomy is a minimally invasive surgery that is performed under general anesthesia. Your surgeon makes two or three tiny 5mm incisions in your lower abdomen (one near each hip bone and a third incision just below your navel) through which slim surgical instruments are introduced to perform the surgery.
First, a thin flexible tube with a lighted camera at the tip is inserted through the incision near your belly button and the images taken by the camera are projected onto a video monitor in the operating room in order to guide your surgeon throughout the surgery.
After your surgeon surveys the ovaries and surrounding pelvic structures, specialized tools are introduced through the small incisions (called portals) on either side of your abdomen. These tools are used to trim and remove any unwanted tissue which is taken out through the portals.
Once the ovaries are removed, the instruments are withdrawn and each portal is closed with a single absorbable stitch before being dressed with a bandage. You are then transferred to the recovery room where you will remain until your anesthesia wears off before being allowed to go home.
Laparoscopic Oophorectomy recovery
After our out-patient oophorectomy, our patients always go home the same day. This is very different than patients who have a traditional non-laparoscopic procedure as they will require a two or three-day hospital stay. Though an overnight stay is required for many laparoscopic surgeries.
In the days following our procedure, you’ll transition from resting to light exercising, being careful to avoid any strenuous activities, and lifting. Nearly all of our patients are 100% back to their normal routine within a couple of weeks after surgery.
We will see you for your first post-op follow up one week after your procedure to check your progress. At that time, we will discuss when you can go back fully to your and resuming sexual intercourse.
What are the advantages of having a laparoscopic oophorectomy?

Laparoscopic surgery offers many advantages over a traditional open abdominal surgical approach that uses a large bikini line incision for ovary removal.
The advantages of our laparoscopic oophorectomy over open surgery include:
- Requiring just two or three tiny incisions that are usually undetectable after six months.
- Having a shorter surgery with less anesthesia exposure (because working through tiny incisions means less time is spent getting in and out of your pelvic region)
- Minimal blood loss (due to much smaller incisions and less manipulation of your pelvic organs)
- Less pain after surgery (due to smaller incisions that leave the abdominal muscles mostly intact)
- Giving your surgeon a better view within your pelvic area as compared to with a single abdominal incision (because the laparoscope can be positioned in several different locations within your pelvis, offering a 360-degree view of some structures)
- A quicker recovery time (most patients are up and about the day after surgery and 100% back to their regular routine within two weeks.
When it comes to gynecologic surgery, there is no substitute for experience

Dr. Thais Aliabadi and Dr. Ramon Yera are recognized experts with an international reputation in minimally invasive OB/GYN surgery, having performed thousands of laparoscopic procedures over twenty years.
The recipients of dozens of awards for medical excellence and patient satisfaction, Drs. Aliabadi and Yera have joined forces to create the Outpatient Hysterectomy Center, a world-class surgical practice dedicated exclusively to women’s health.
Doctors Aliabadi and Yera specialize in leading-edge minimally invasive surgeries that offer patients shorter recovery times, less pain, and the least interruption to their daily lives.
If you are considering gynecologic surgery, you owe it to yourself to learn about the minimally invasive surgical treatment options available today.
If you wish to schedule a consultation to learn how we can help you or to establish care with us, please request a consultation online or call us at 844-541-7900.